EOY Outcome Data Report
Estimating End-of-Year Mathematics Attainment (η) from PAT Scores and Teacher Ratings
1 Introduction
Context & Objective
We need a defensible way to identify students at risk of not meeting end-of-year maths expectations. This report explains how we construct an outcome-side attainment measure (η) from PAT + teacher ratings, and how that outcome is used to calibrate screener cutoffs.
- η (eta) = latent end-of-year attainment on a PAT scale-score ruler.
- Risk bands (High/Moderate/Low) are derived from η; they are not a separate construct.
- Working criterion: “below the 20th percentile” is the provisional definition of “behind expected” (pending external validation).
2 Data Sources & Quality Overview
The Sparse Data Challenge
Most students have only teacher ratings and no PAT. That makes η estimation fundamentally an evidence synthesis problem: PAT is a strong ruler but sparse; ratings are widespread but noisy.
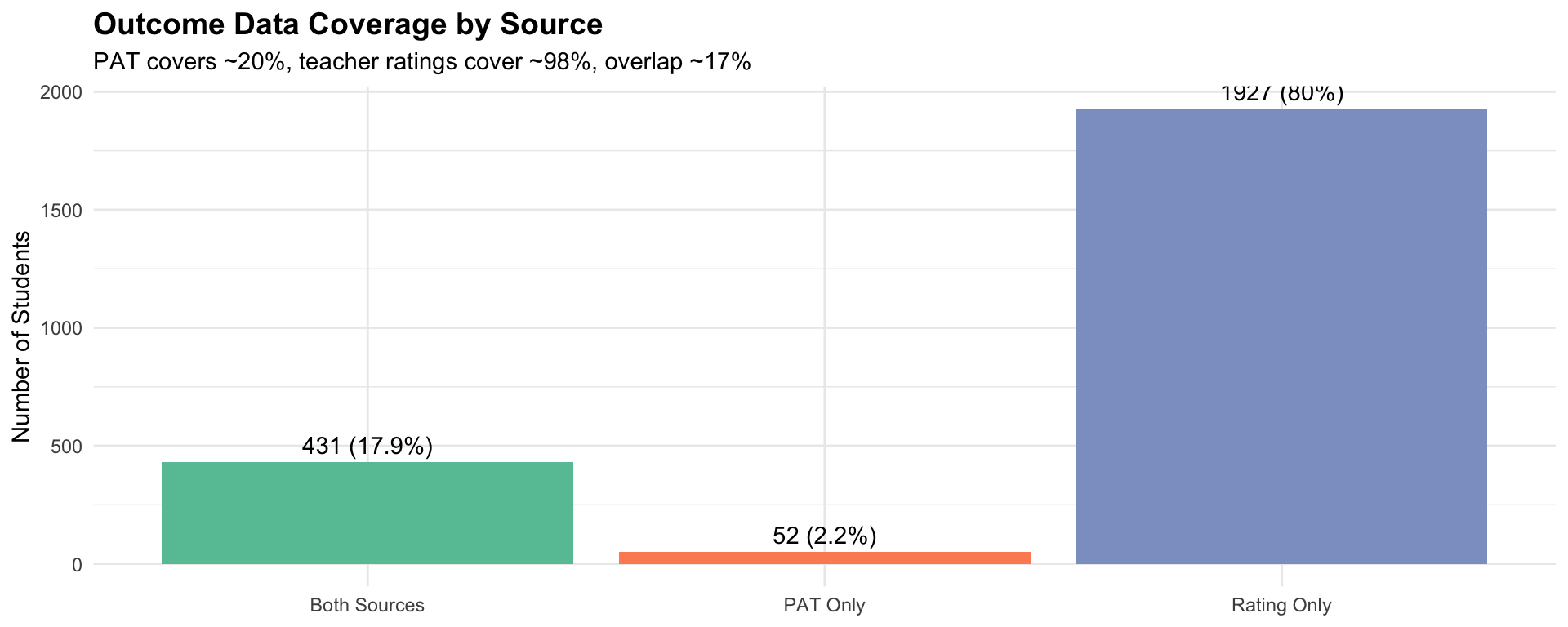
The Problem: How do we create a unified risk metric when: - PAT scores (standardised tests) cover only ~20% of students - Teacher ratings cover ~98% but are ordinal and subject to rater bias - Only ~17% have both sources for cross-validation
Data Sources
PAT (Progressive Achievement Tests): Standardised mathematics assessments developed by ACER. Two variants in this study:
- PAT Early Years (Foundation): Reference-group normed (self-selecting schools)
- PAT Maths 4th Edition (Year 1): Nationally normed (2022 Australian norms)
Strengths: Objective and standardised; interval scale (differences meaningful); established norms (Year 1: μ=99.5, σ=11.4); conditional standard errors.
Limitations: Low coverage (~20%); timing heterogeneity (6-month window); Foundation uses self-selecting reference groups; PAT variants may not be perfectly comparable.
Data collection context: Schools collected PAT data at different frequencies based on existing practices — some not at all, some once per year, others twice. Multiple PAT versions in use. The Janison system initially created one set of fields, then added EOY-prefixed fields. “Occasion 1” and “Occasion 2” refer to chronological order based on actual testing dates, not field names.
Teacher achievement ratings: 5-point ordinal scale (1=Well below expected, 5=Well above expected).
Strengths: High coverage (~98%); classroom context (multiple observations over time); holistic judgement beyond test performance.
Limitations: Ordinal scale (not interval); rater severity bias (ICC ≈ 0.20, ~20% of variance is school-level); subjective (within-class comparisons, not national norms).
student_outcome.parquet
7,971 students × 10 columns. All text fields including numeric scores and dates. Each student has one row with separate columns for Occasion 1 and Occasion 2 (EOY). Key fields: Identifier (student GUID), Standardised test result available (PAT form), Date of Testing / Scaled Score / Percentile Rank (first administration), EOY-prefixed equivalents (second administration), Achievement Scale (teacher rating 1-5).
See Appendix A.1 for full field-level documentation.
student_outcome_pat.parquet
Long format (7971 students × 2 occasions = 15942 rows × 13 columns). Typed fields (dates, numerics), quality flags (pat_type_missing, pat_year_imputed, pat_date_imputed, pat_date_suspect, pat_score_percentile_mismatch, pat_date_off_screener_year, no_screener_resp). Key fields: student_id, year_level, pat_occasion (1 or 2), pat_type, pat_date, pat_scaled_score, pat_percentile.
See Appendix A.1 for full field-level documentation.
student_outcome_teacher.parquet
7,971 students × 5 columns. One row per student. Key fields: student_id, year_level, teacher_rating (1-5), teacher_rating_label, has_teacher_rating.
See Appendix A.1 for full field-level documentation.
Coverage & Completeness
| source_flag | foundation | year1 | total |
|---|---|---|---|
| Both | 171 | 260 | 431 |
| PAT_only | 32 | 20 | 52 |
| Rating_only | 965 | 962 | 1927 |
| Issue | Details | Cleaning Rule |
|---|---|---|
| Placeholder scores | Scores of 0 or 1 (implausible for PAT ~50-150) | Convert to NA |
| PAT type discrepancy | Valid score but type blank/wrong | Override to “PAT type missing”, flag |
| Percentile formatting | Mixed: “43”, “24th”, “6th” | Strip non-numeric suffix |
| Date formatting | 5+ formats including timestamps and month-only | Multi-format parse via lubridate |
| Ambiguous dates | ~39% of dates have day and month ≤12 | Assume d/m/Y (Australian). 485 unambiguous dates support this. |
| Month-only (no year) | 29 records | Impute year from screener year (per-student from attempted responses; global fallback), flag pat_year_imputed |
| Month-only (with year) | No day | Impute day to 15th, flag pat_date_imputed |
| Suspect dates | Year < 2024 or year >= screener_year + 1 | Flag, set date = NA |
| Score/percentile mismatch | 189 records missing one | Flag |
Data processing via R/clean_outcome_data.R. Date imputation salvaged 18 of 29 month-only records.
Timing Uncertainty
We do not project growth from earlier PAT administrations. Instead, earlier tests carry more uncertainty about end-of-year attainment, implemented as a variance inflation term proportional to time distance.
The following section explores the outcome data in detail, with each analysis motivating a specific modelling decision.
3 Data Exploration
Each sub-section concludes with a modelling implication that links the finding to a specific design choice in Section 4.
Outcome Distributions
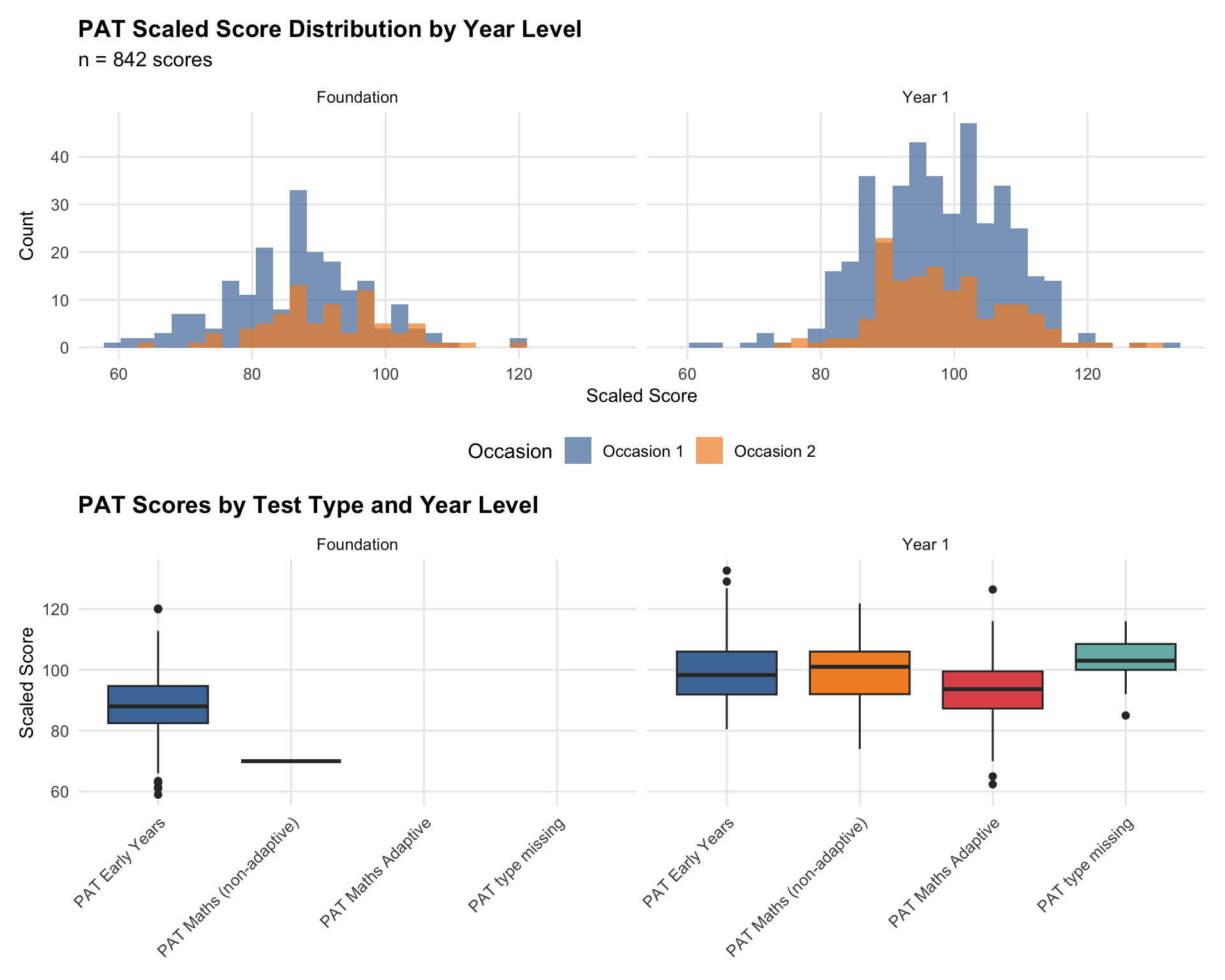
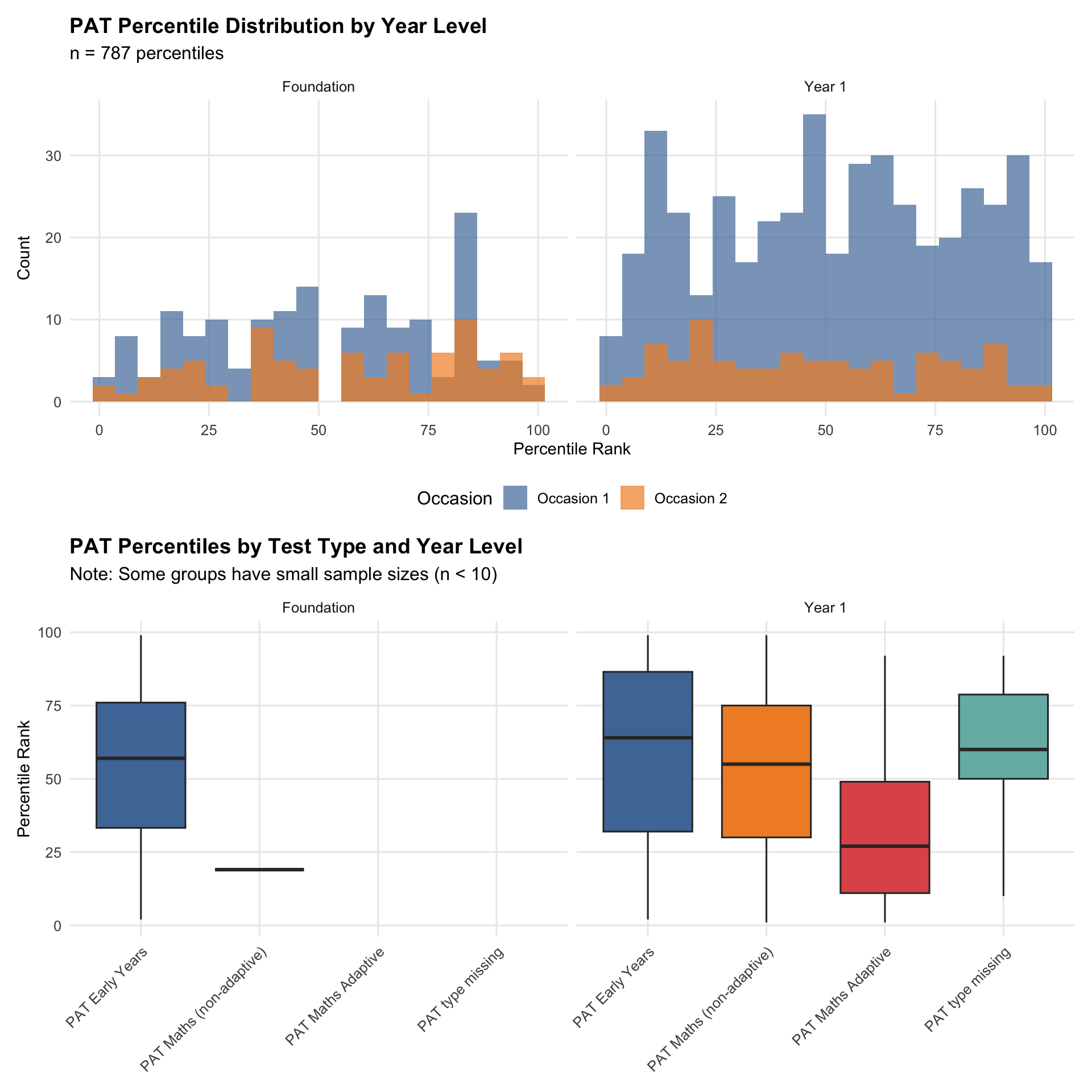
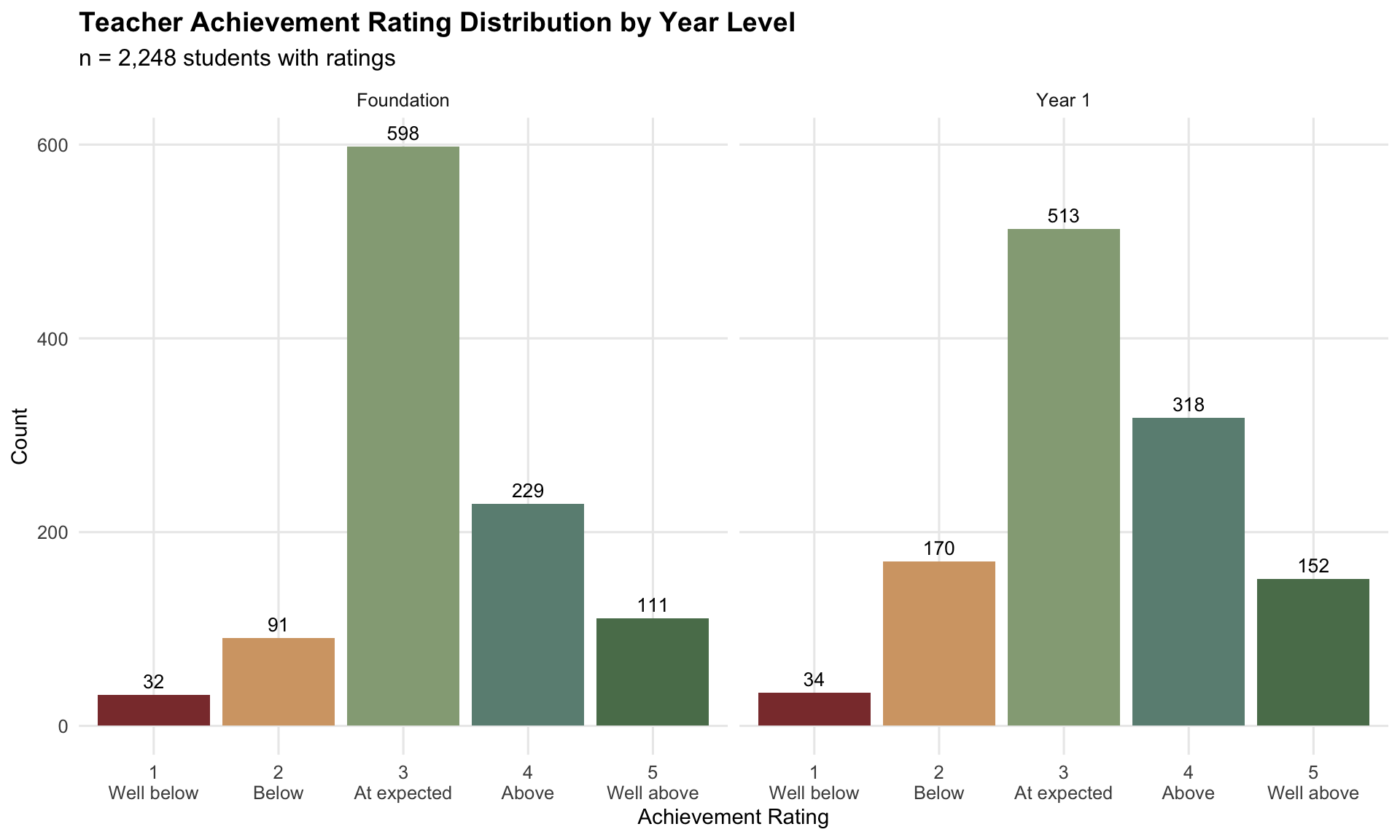
PAT scaled scores are approximately normal within year level, supporting a linear mixed model (Stage 1). Teacher ratings are ordinal with a unimodal distribution centred on “3 - At expected”, motivating a cumulative link (ordered probit) model (Stage 2). See Section 4.
School-Level Data Completeness
| outcome_type | Schools | Students |
|---|---|---|
| No outcome data | 89 | 4,625 |
| Teacher ratings only | 44 | 2,215 |
| Both PAT and teacher ratings | 15 | 969 |
| PAT only | 4 | 158 |
Warning: Removed 4 rows containing missing values or values outside the scale range
(`geom_bar()`).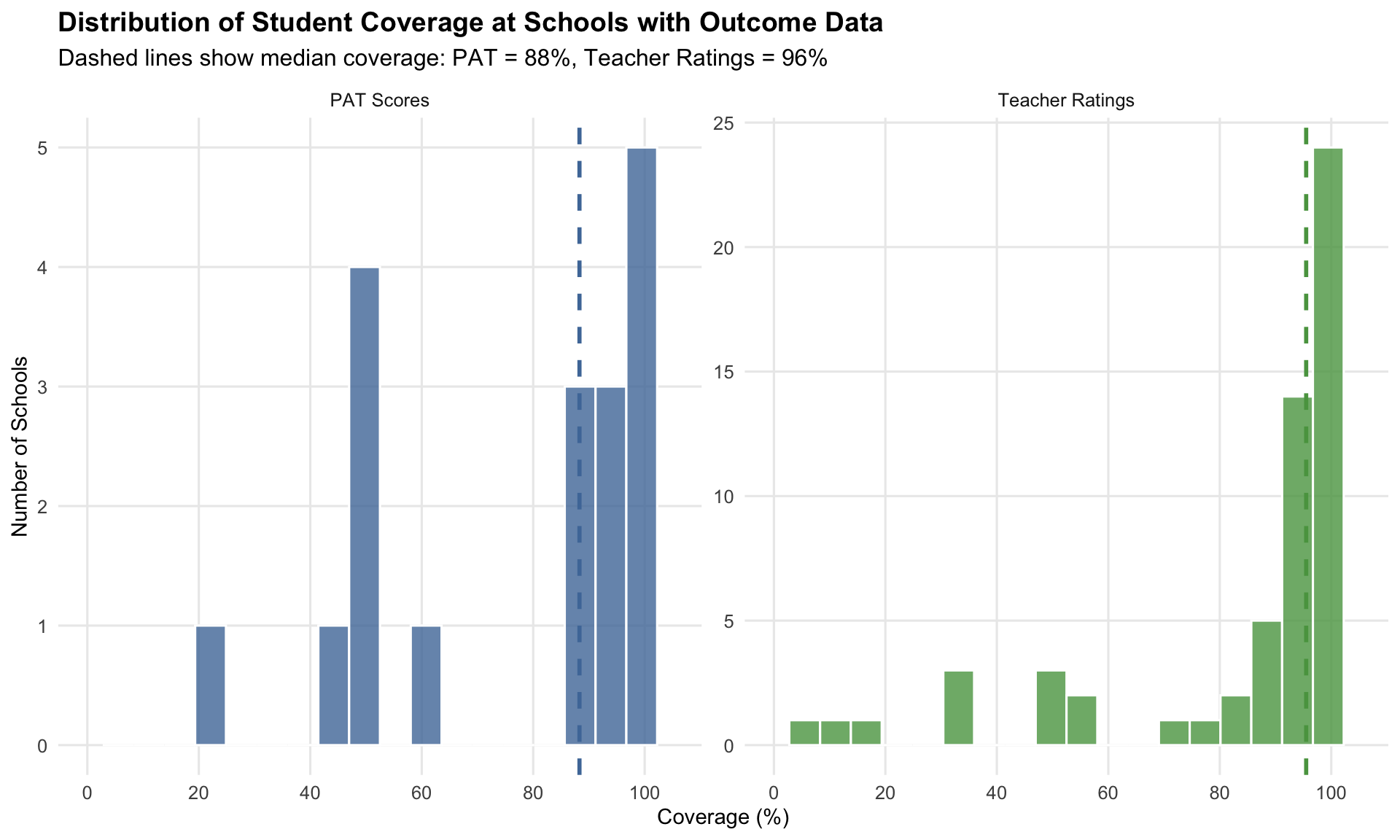
63 of 152 schools provided any outcome data. PAT data is sparse (19 schools); teacher ratings are more common (59 schools). Most schools that provide data do so comprehensively — median PAT coverage 88%, median teacher rating coverage 96%.
PAT availability is entirely school-driven: schools either administer PAT or they do not. This motivates inclusion of school random intercepts and consideration of inverse-probability weighting (IPW) to address potential selection bias. See Section 4.
Overlap Sample Profile
| Outcome Source | n Students | % of Total |
|---|---|---|
| PAT only | 194 | 2.4 |
| Teacher rating only | 1,771 | 22.2 |
| Both (overlap) | 587 | 7.4 |
| Total with any outcome | 2,552 | 32.0 |
| Rating | n | Mean PAT Score | SD | Mean Percentile |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 22 | 82.6 | 10.7 | 21.6 |
| 2 | 60 | 90.6 | 9.6 | 33.1 |
| 3 | 298 | 94.3 | 10.1 | 51.1 |
| 4 | 175 | 97.4 | 11.1 | 61.3 |
| 5 | 32 | 109.6 | 9.0 | 81.1 |
| Year Level | n | Spearman ρ (Scale) | Pearson r (Scale) | Spearman ρ (Percentile) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Foundation | 168 | 0.287 | 0.317 | 0.327 |
| Year 1 | 413 | 0.407 | 0.412 | 0.445 |
Warning: Removed 67 rows containing non-finite outside the scale range
(`stat_boxplot()`).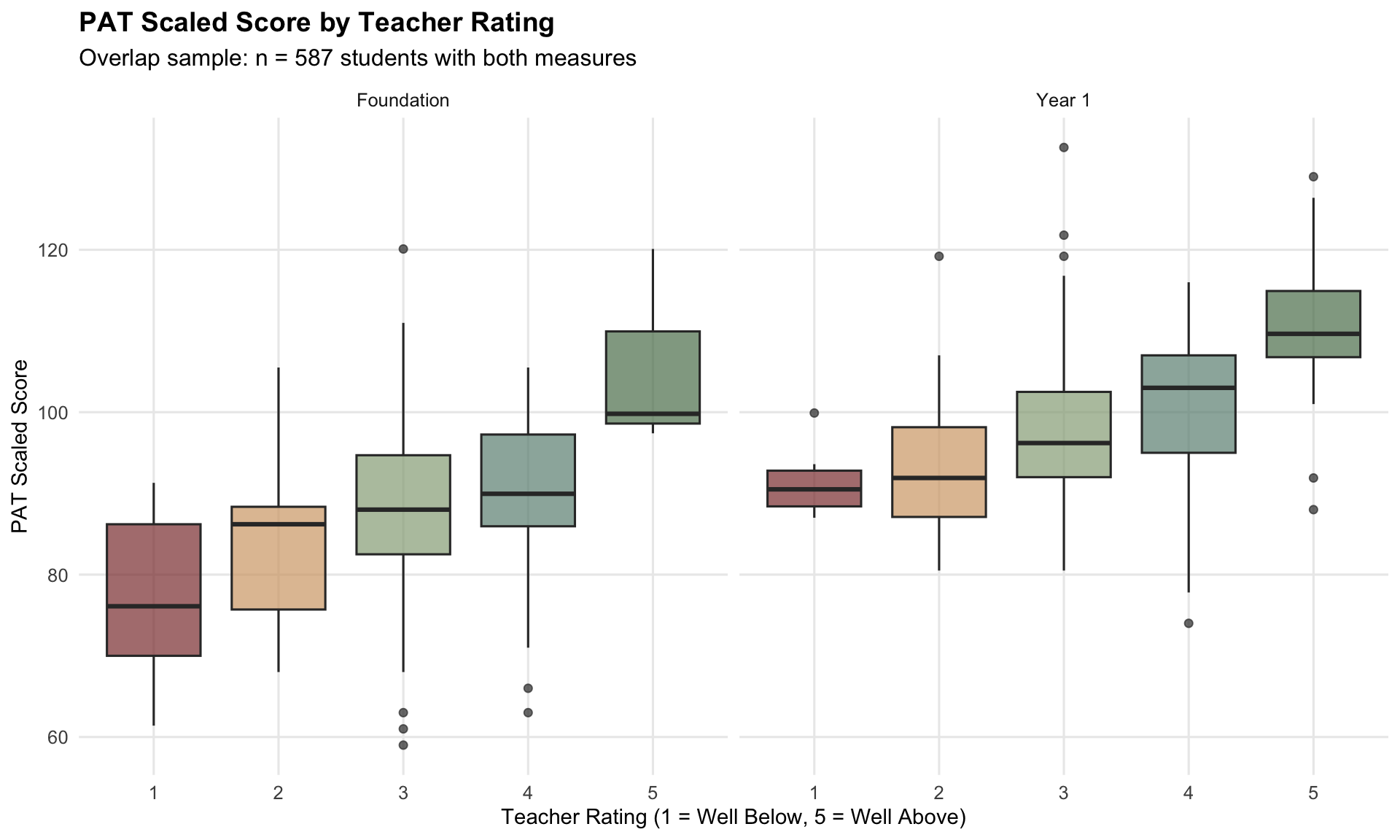
Teacher Ratings Among Low PAT Percentiles (Foundation)
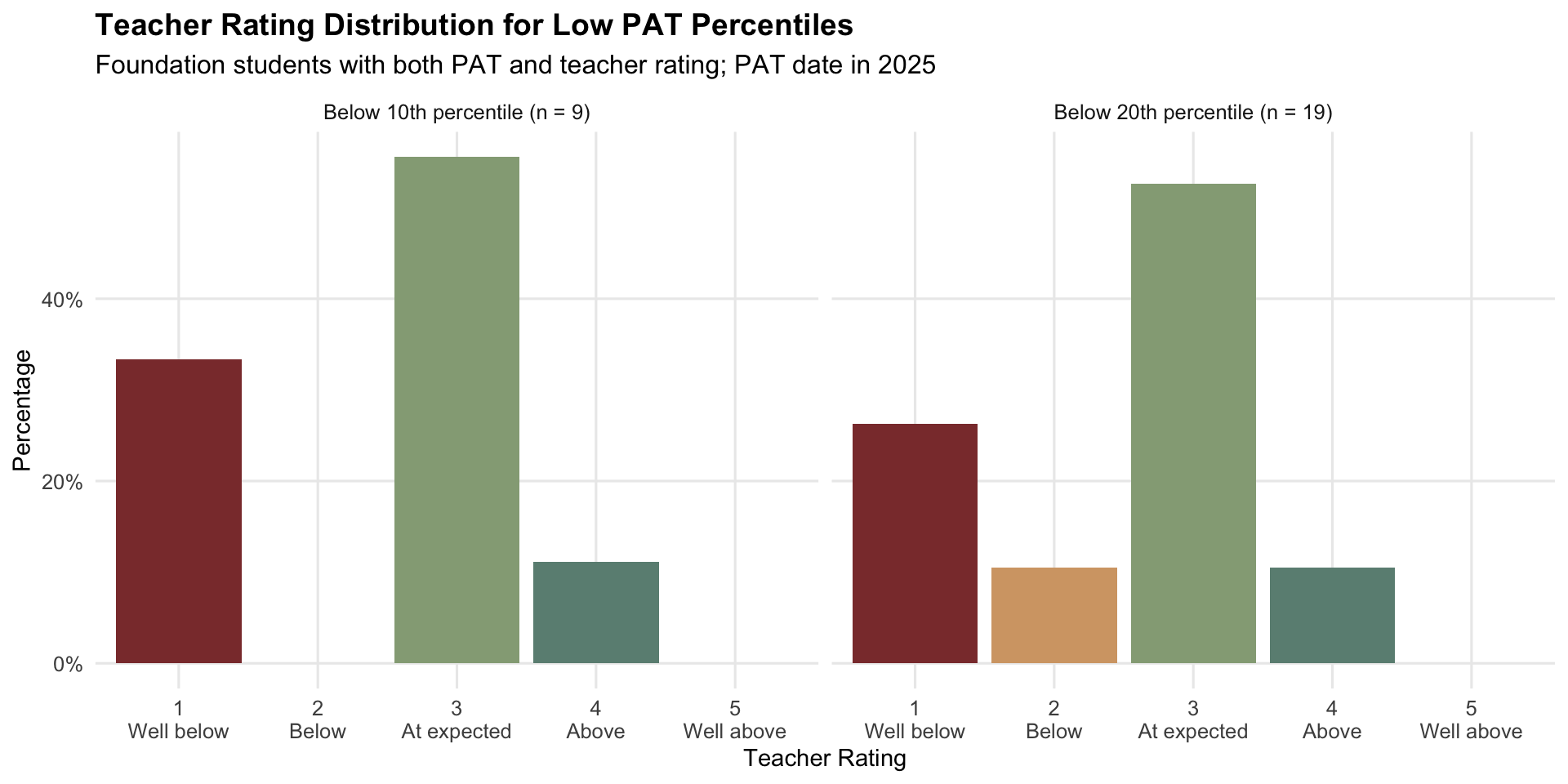
Monotonic PAT-rating relationship confirms that teacher ratings carry information about the same latent construct. The overlap sample (~520 students) is sufficient for calibration but not large — small changes to this sample (e.g., excluding a school) can shift prevalence materially. See Section 4, Stage 2.
Missingness Mechanism Analysis
| Variable | SMD | n (with PAT) | n (without PAT) | Flag |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 0.262 | 709 | 6995 | MODERATE |
Interpretation: |SMD| < 0.1 = negligible, 0.1-0.2 = small, 0.2-0.5 = moderate, >0.5 = large imbalance.
ICC = 0.985
Substantial school-level clustering in PAT availability. Missingness is NOT MCAR — school is a strong predictor of which students have PAT data.
| Year Level | Without PAT | With PAT | % with PAT |
|---|---|---|---|
| Unknown | 7,253 | 714 | 9 |
MCAR is rejected. PAT availability is driven by school policy, not student characteristics, making MAR (Missing At Random conditional on school) plausible. This motivates school random intercepts in both Stage 1 and Stage 2 of the model. See Section 4.
PAT Type Stratification
| PAT Type | n | Spearman ρ | Pearson r | Mean PAT | SD PAT |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PAT Early Years | 269 | 0.214 | 0.245 | 91.7 | 12.1 |
| PAT Maths (non-adaptive) | 207 | 0.514 | 0.523 | 99.1 | 9.0 |
| PAT Maths Adaptive | 44 | 0.422 | 0.519 | 99.4 | 8.5 |
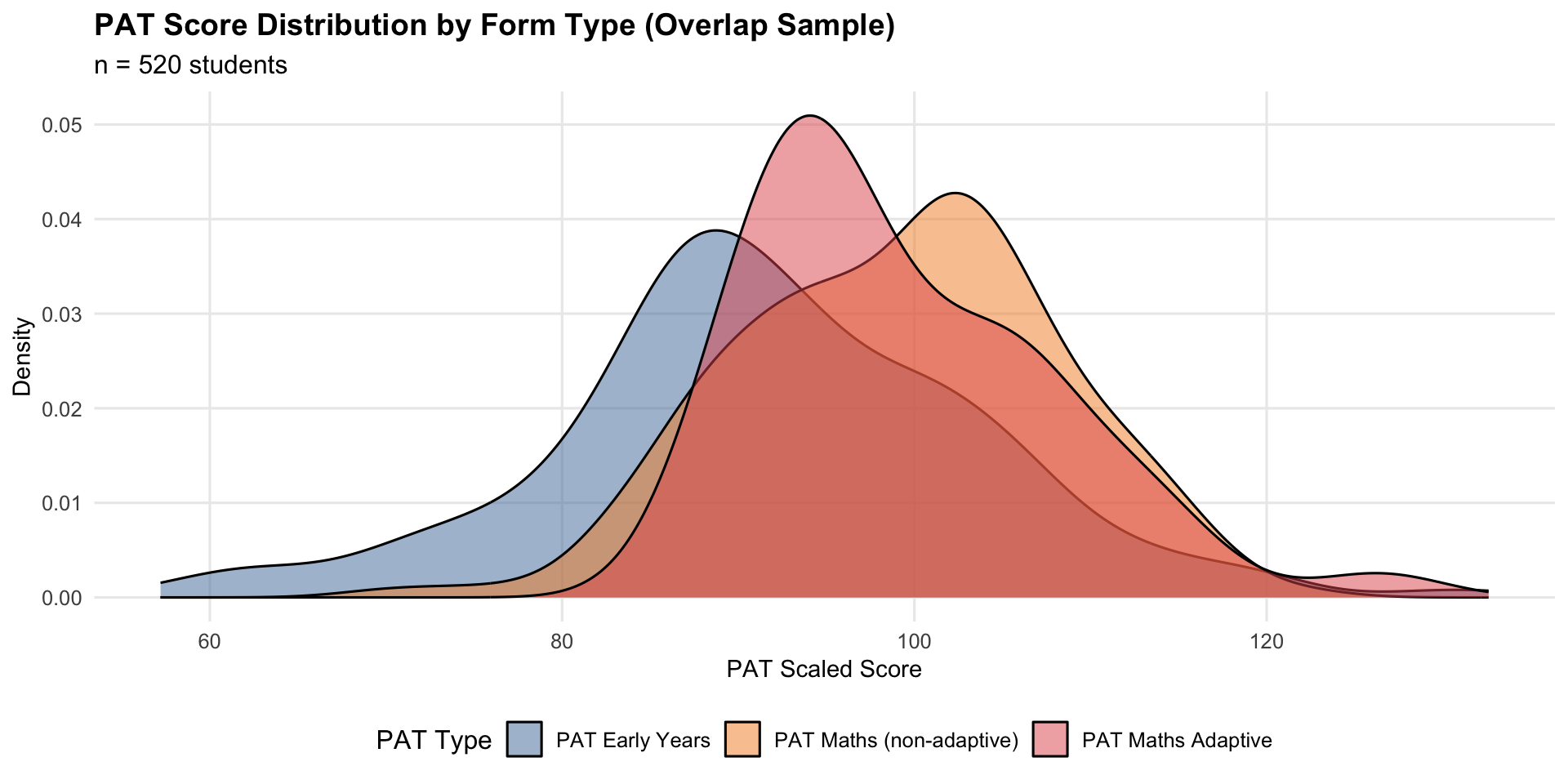
Correlation strength and score distributions vary by PAT type. This motivates including pat_type as a fixed effect in Stage 1 to account for systematic offsets between PAT variants. See Section 4.
School-Level Rater Effects
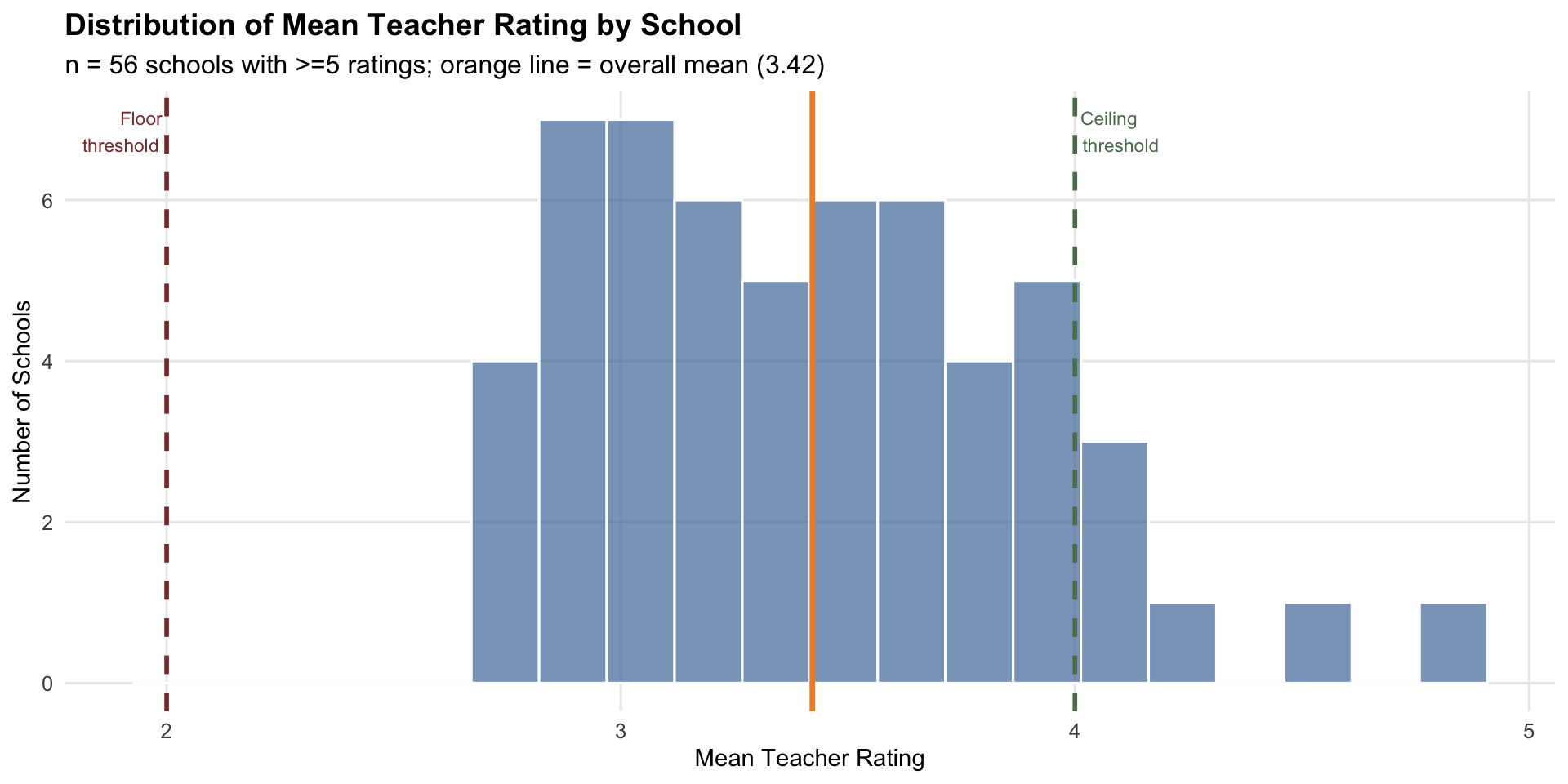
| Component | Variance | % of Total |
|---|---|---|
| School | 0.176 | 20.3 |
| Residual (within-school) | 0.690 | 79.7 |
| Total | 0.866 | 100.0 |
ICC for teacher ratings = 0.203: 20.3% of rating variance is between schools, indicating meaningful school-level rater effects.
| Issue | Schools | % of Schools |
|---|---|---|
| Floor effect (max rating <= 2) | 0 | 0.0 |
| Ceiling effect (min rating >= 4) | 1 | 1.8 |
| No variation (SD = 0) | 0 | 0.0 |
School explains ~20% of teacher rating variance (ICC ≈ 0.20). This is substantial rater severity bias that would distort risk classification if ignored. Stage 2 includes school random intercepts to absorb rater severity. See Section 4.
PAT Testing Timeline
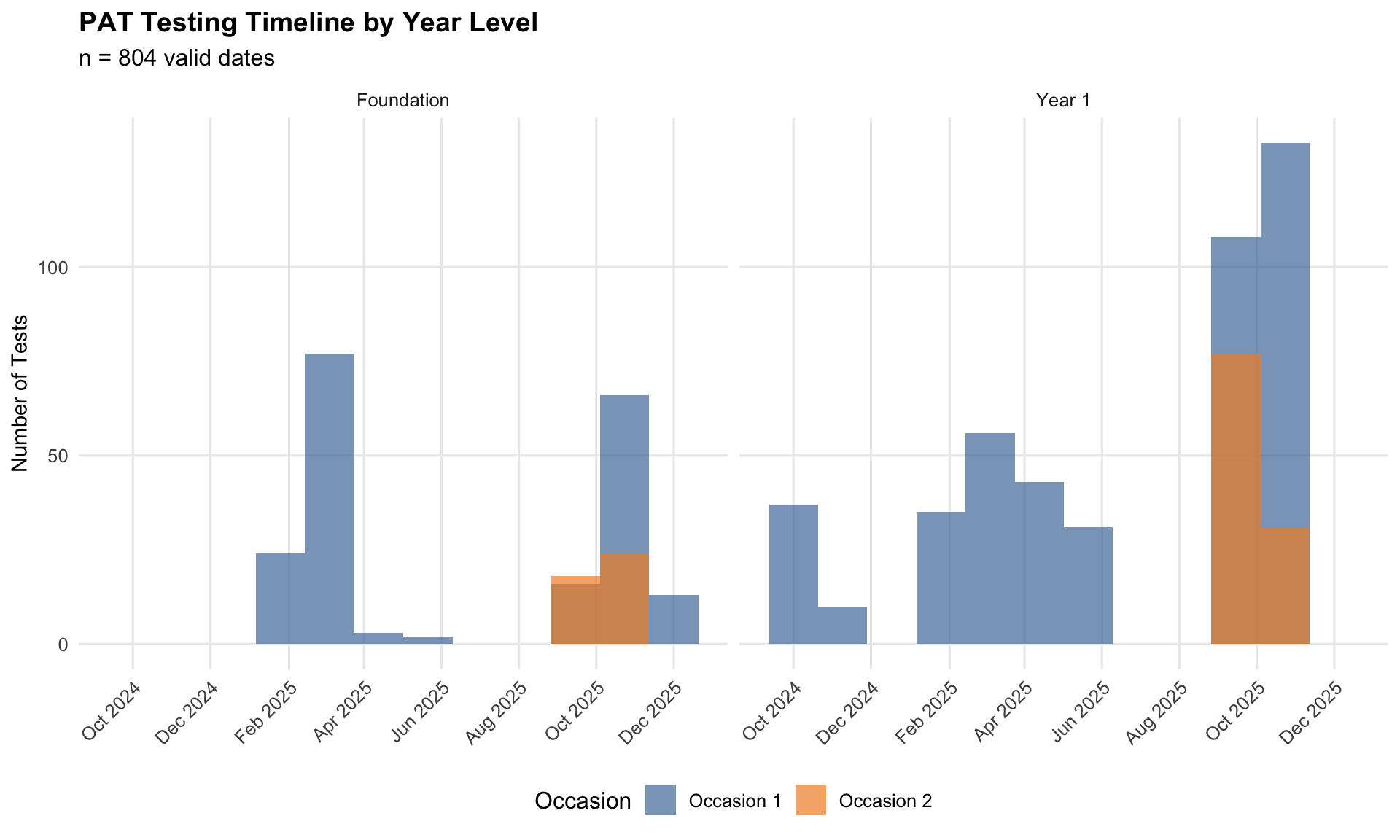
Key Observations:
- Occasion 1 (chronologically first) shows wide variance in timing (Oct 2024 - Dec 2025)
- Occasion 2 (chronologically second) tightly clustered in Oct-Nov 2025
- Schools administered first PAT at various points (BOY, MOY, or EOY) depending on schedule
The 6+ month spread in PAT administration dates means earlier tests are less informative about end-of-year attainment. This motivates the time-decay variance term (σ_time) in Stage 1: uncertainty increases proportionally with distance from the EOY reference date. See Section 4.
4 Model Specification
η is estimated via a three-stage hierarchical calibration:
Motivated by: approximately normal PAT distributions (3.1), school-level missingness clustering (3.4), and timing variance (3.7).
Stage 1 — PAT Model:
lmer(pat_scaled_score ~ year_level + pat_type + years_to_eoy + (1|school_id))- Extracts η in PAT scale-score units
- Handles timing heterogeneity via time-decay uncertainty
- Accounts for school clustering
Motivated by: ordinal rating distribution (3.1), school-level rater effects with ICC ≈ 0.203 (3.6), and validated overlap sample (3.3).
Stage 2 — Rating Calibration:
clmm(rating ~ 1 + eta_from_pat + (1|school_id))- Ordered probit model learns rating → PAT mapping
- School random effects capture rater severity
- Applied to rating-only students via conditional expectation from the ordinal model
Combines both signals for overlap students; rating-only students (3.4) receive estimates via Stage 2 calibration alone.
Stage 3 — Precision Weighting: - For students with both sources, combine via inverse-variance weighting: η_combined = (w_PAT · η_PAT + w_rating · η_rating) / (w_PAT + w_rating) - Where w = 1 / SE²
Rating-Only Estimation
Rating-only students receive η estimates via conditional expectation from the ordinal rating model. For each teacher rating value, the model computes the expected η conditional on that rating and school-specific rater severity. This produces a “soft label” distribution accounting for ordinal-to-continuous transformation, school-level rater severity, and uncertainty in the calibration model.
See Appendix A.3: Mathematical Model Specifications for full model formulations and Diagnostics for uncertainty discussion.
5 Results
Classification Method
Risk classification uses the Single-η Framework: η is in PAT scale-score units, and risk z-scores are computed at scoring time using NORM_FRAME_EOY.
z-score cuts (exact percentiles): - High risk: z < qnorm(0.10) = -1.2816 (bottom 10%) - Moderate risk: -1.2816 ≤ z < qnorm(0.20) = -0.8416 (10th-20th percentile) - Low risk: z ≥ -0.8416 (above 20th percentile)
Equivalent scale-score cuts by year level: - Foundation: High < 79.5, Moderate < 83.9 (using μ=92.4, σ=10.1) - Year 1: High < 84.9, Moderate < 89.9 (using μ=99.5, σ=11.4)
| Band | z Criterion | Percentile | Foundation η | Year 1 η |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| High Risk | z < -1.2816 | Below 10th | < 79.5 | < 84.9 |
| Moderate Risk | -1.2816 ≤ z < -0.8416 | 10th-20th | 79.5 - 83.9 | 84.9 - 89.9 |
| Low Risk | z ≥ -0.8416 | Above 20th | ≥ 83.9 | ≥ 89.9 |
The current risk cuts are purely norm-referenced based on ACER reference group distributions. They have not been validated against external criteria such as:
- Year 2 standardised test outcomes
- Teacher referrals for intervention
- Actual intervention receipt or effectiveness
- Growth trajectories over time
Implication: These cuts identify students at the bottom of the distribution (statistical risk), not students who are necessarily at educational risk (clinical significance). Until criterion validation is performed, interpret risk classifications as relative standing, not absolute educational need.
Cut validation data not available.
Risk Prevalence
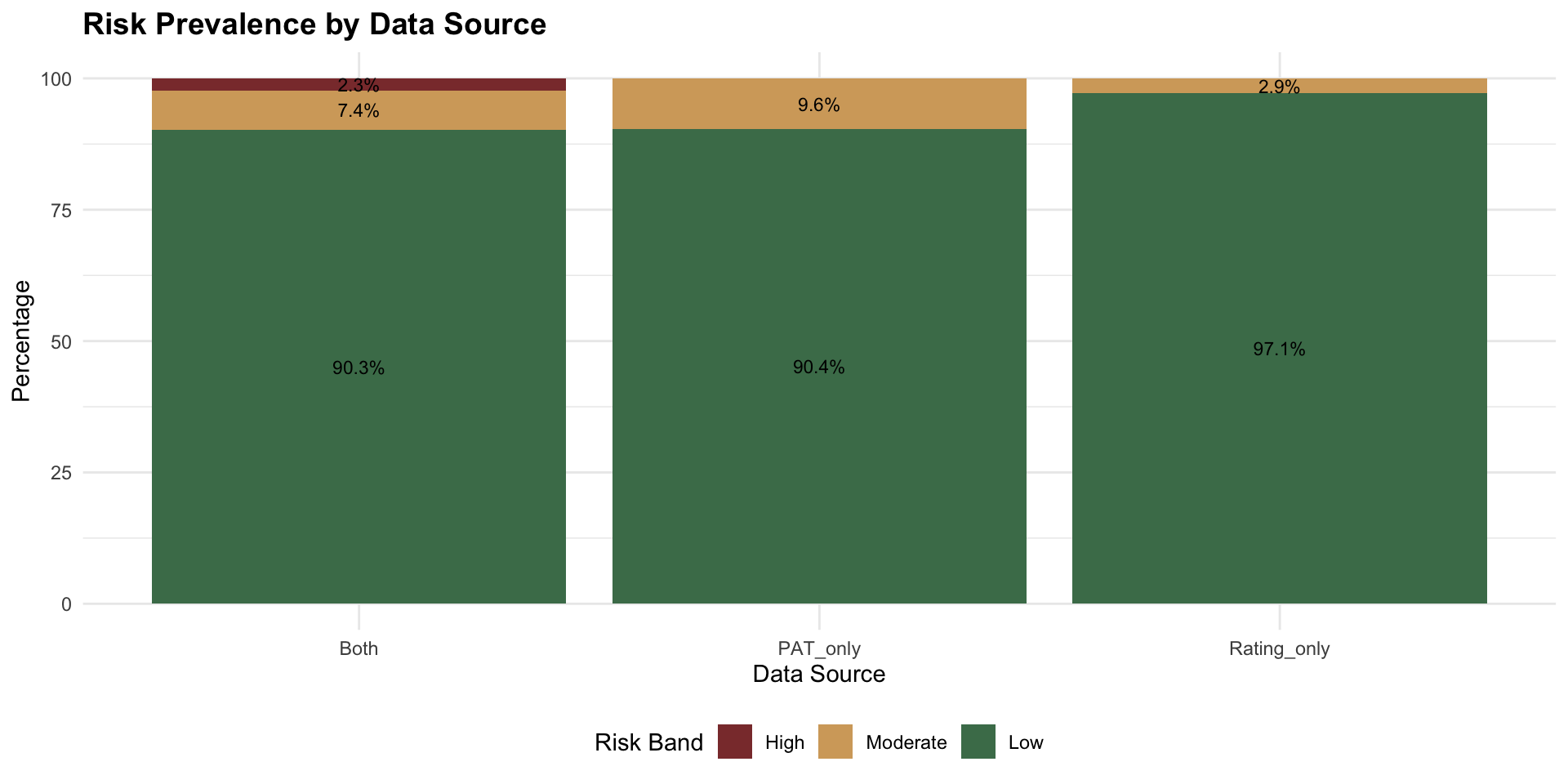
**Reference values** (from NORM_FRAME_EOY):
- Foundation: μ = 92.4, σ = 10.1
- Year 1: μ = 99.5, σ = 11.4Benchmarks
This analysis presents risk classifications using two complementary benchmarks. ACER Norm-Referenced compares students to Australian national reference groups (2021-2022) using fixed z-score cuts at the 10th and 20th percentiles. Cohort-Referenced identifies relative need within the current student population using within-cohort percentiles derived from conclusive students per year level, with inconclusive students excluded from quantile calculation.
| year_level | ACER High % | ACER Moderate+ % | Cohort High % | Cohort Moderate+ % | Inconclusive % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| foundation | 0.5 | 4.0 | 3.2 | 15.2 | 5.6 |
| year1 | 0.3 | 4.4 | 4.5 | 19.2 | 3.8 |
**Overall agreement:** 82.2% (excluding inconclusive)
ACER bands identify students below national expectations (absolute deficit). Cohort bands identify students at the bottom of this cohort (relative need). A student can be "Low" risk by ACER standards but "High" risk within their cohort if the cohort overall performs below national norms.Validity
Convergent Validity
For students with PAT scores, η is derived directly from the PAT scale score via the mixed model. The correlation with raw scale scores should be very high.
Known-Groups Validity
The traditional “known-groups” expectation that Year 1 η > Foundation η applies because η is in PAT scale-score units (not percentiles). Expected differences: Foundation median η ≈ 92.4, Year 1 median η ≈ 99.5, a difference of ≈ 7 scale points reflecting typical growth. Risk z-scores are year-level specific (computed using NORM_FRAME_EOY), so a Foundation student at z=0 is at the 50th percentile for Foundation, and a Year 1 student at z=0 is at the 50th percentile for Year 1.
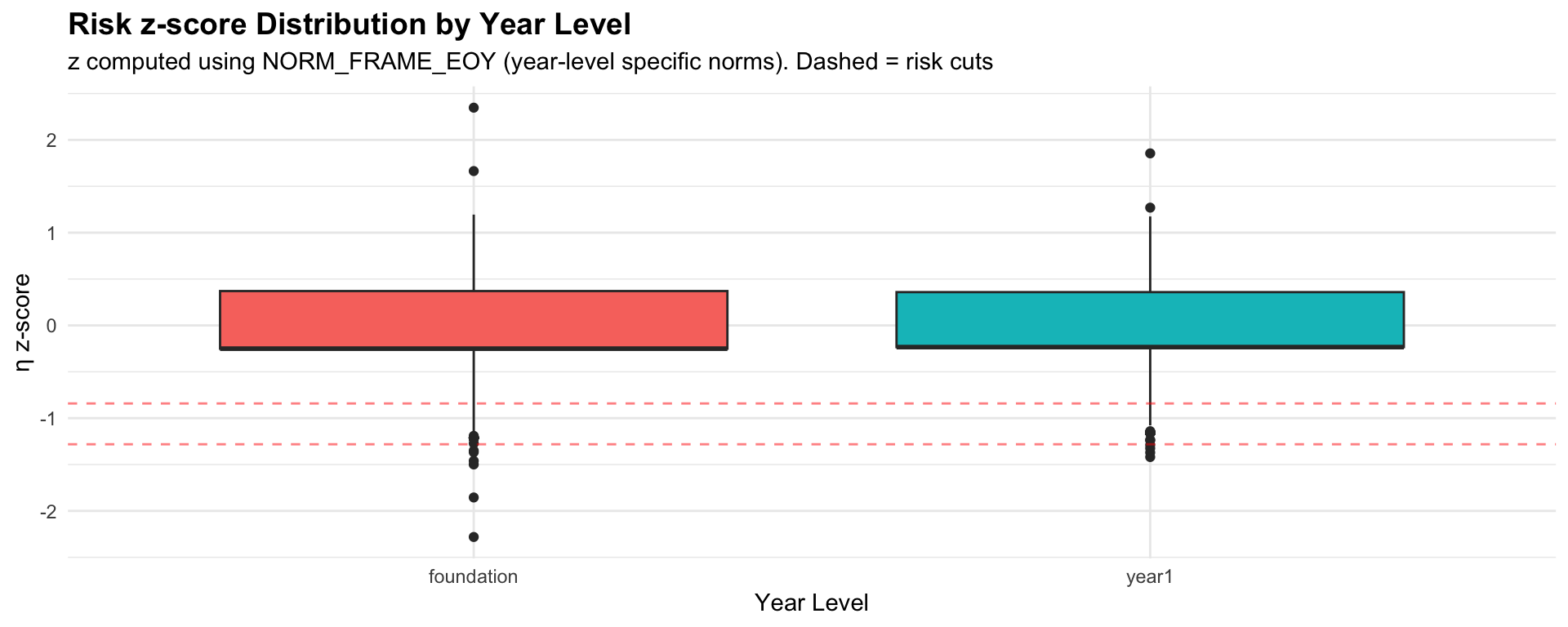
Sensitivity Analysis
Sensitivity analyses were conducted across PAT inclusion rules (window_180d, year_2025, no_cap) and specification variants (prior type, IPW weighting, rater-level effects). Results were robust across all tested scenarios.
| Variant | Benchmark | Band | n | % |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Default (pat_empirical + school + IPW off) | ACER | High | 10 | 0.4 |
| Default (pat_empirical + school + IPW off) | ACER | Moderate | 92 | 3.8 |
| Default (pat_empirical + school + IPW off) | ACER | Low | 2308 | 95.8 |
| Default (pat_empirical + school + IPW off) | Cohort | High | 93 | 3.9 |
| Default (pat_empirical + school + IPW off) | Cohort | Moderate | 323 | 13.4 |
| Default (pat_empirical + school + IPW off) | Cohort | Low | 1882 | 78.1 |
| Default (pat_empirical + school + IPW off) | Cohort | Inconclusive | 112 | 4.6 |
| Sensitivity: IPW on | ACER | High | 9 | 0.4 |
| Sensitivity: IPW on | ACER | Moderate | 93 | 3.9 |
| Sensitivity: IPW on | ACER | Low | 2308 | 95.8 |
| Sensitivity: IPW on | Cohort | High | 92 | 3.8 |
| Sensitivity: IPW on | Cohort | Moderate | 336 | 13.9 |
| Sensitivity: IPW on | Cohort | Low | 1870 | 77.6 |
| Sensitivity: IPW on | Cohort | Inconclusive | 112 | 4.6 |
| Sensitivity: prior=ACER | ACER | High | 65 | 2.7 |
| Sensitivity: prior=ACER | ACER | Moderate | 265 | 11.0 |
| Sensitivity: prior=ACER | ACER | Low | 2080 | 86.3 |
| Sensitivity: prior=ACER | Cohort | High | 69 | 2.9 |
| Sensitivity: prior=ACER | Cohort | Moderate | 362 | 15.0 |
| Sensitivity: prior=ACER | Cohort | Low | 1867 | 77.5 |
| Sensitivity: prior=ACER | Cohort | Inconclusive | 112 | 4.6 |
| Sensitivity: rater_level=none | ACER | High | 9 | 0.4 |
| Sensitivity: rater_level=none | ACER | Moderate | 37 | 1.5 |
| Sensitivity: rater_level=none | ACER | Low | 2364 | 98.1 |
| Sensitivity: rater_level=none | Cohort | High | 149 | 6.2 |
| Sensitivity: rater_level=none | Cohort | Moderate | 254 | 10.5 |
| Sensitivity: rater_level=none | Cohort | Low | 1895 | 78.6 |
| Sensitivity: rater_level=none | Cohort | Inconclusive | 112 | 4.6 |
Prior sensitivity (rating-only students):
| Risk Band | n | % | Prior |
|---|---|---|---|
| Moderate | 55 | 2.3 | acer |
| Low | 2303 | 97.7 | acer |
| High | 282 | 12.0 | pat_empirical |
| Moderate | 28 | 1.2 | pat_empirical |
| Low | 2048 | 86.9 | pat_empirical |
Note: Rating-only calibration now uses a pat-empirical prior (not ACER) and IPW is disabled by default. This shifts prevalence downward relative to the prior ACER-based calibration.
Probability Outputs
The pipeline also produces probability outputs (e.g., p20_calibrated) estimating the chance a student is below a benchmark cut. Use these for triage under capacity constraints or to express confidence explicitly. Do not treat as externally validated risk until future outcomes are available. The probability-first scheme is available in the pipeline outputs: main output student_scored_probability.parquet with key fields p20, action_tier, severity_level.
6 Diagnostics
Classification reliability analysis reveals 24.5% overall flip rate when using bootstrap resampling. The moderate risk band is particularly unstable:
- Moderate risk flip rate: 77.8% (4 in 5 students would be reclassified with slightly different data)
- High risk flip rate: 12.3%
- Low risk flip rate: 8.7%
Implication: Students classified as “Moderate Risk” are borderline cases with high measurement uncertainty. Do not treat this band as definitively distinct from adjacent categories.
Recommended action: Flag students near decision boundaries (±0.25 SD from cuts) as “borderline” for follow-up assessment.
Classification Stability
Bootstrap analysis (500 replicates with school-clustered resampling) reveals substantial instability in risk band assignments, particularly for students near decision boundaries.
Bootstrap stability (Full refit):
- Overall flip rate: 3.9 %
- Moderate flip rate: 90.2 NA %
- % stable (flip <15%): 96 %
| Band | n | Flip rate (%) |
|---|---|---|
| High | 10 | 96.5 |
| Low | 2308 | 0.0 |
| Moderate | 92 | 90.2 |
| NA | 5557 | NaN |
See Appendix B for full methodology, distance-to-cut diagnostics, and transition matrices.
Borderline Zone
Students within ±0.25 SD of a cut-point are flagged as “borderline” for follow-up assessment.
Rating-Only Uncertainty
Students with only teacher ratings (no PAT) have η estimated via a calibrated rating→PAT crosswalk. These estimates are usable but are the most sensitive to modelling assumptions. Treat rating-only bands as screening signals, not final placement decisions. Prefer follow-up assessment for High/Moderate rating-only students. School-level rater effects are material and are adjusted for in the main workflow.
Key uncertainty drivers: Rater severity (some schools use the 1-5 scale more leniently/harshly); ordinal granularity (rating=3 spans a wide middle range; extremes are more informative); weak signal (ratings explain limited variance in PAT outcomes; estimates rely heavily on calibration assumptions).
p20 Calibration
Calibration status: ok
- Intercept: -0.899
- Slope: 0.678
- Brier (raw): 0.0725
- Brier (calibrated): 0.072
- Mean p20 (raw): 0.102
- Mean p20 (calibrated): 0.081
- Event rate (y20): 0.081
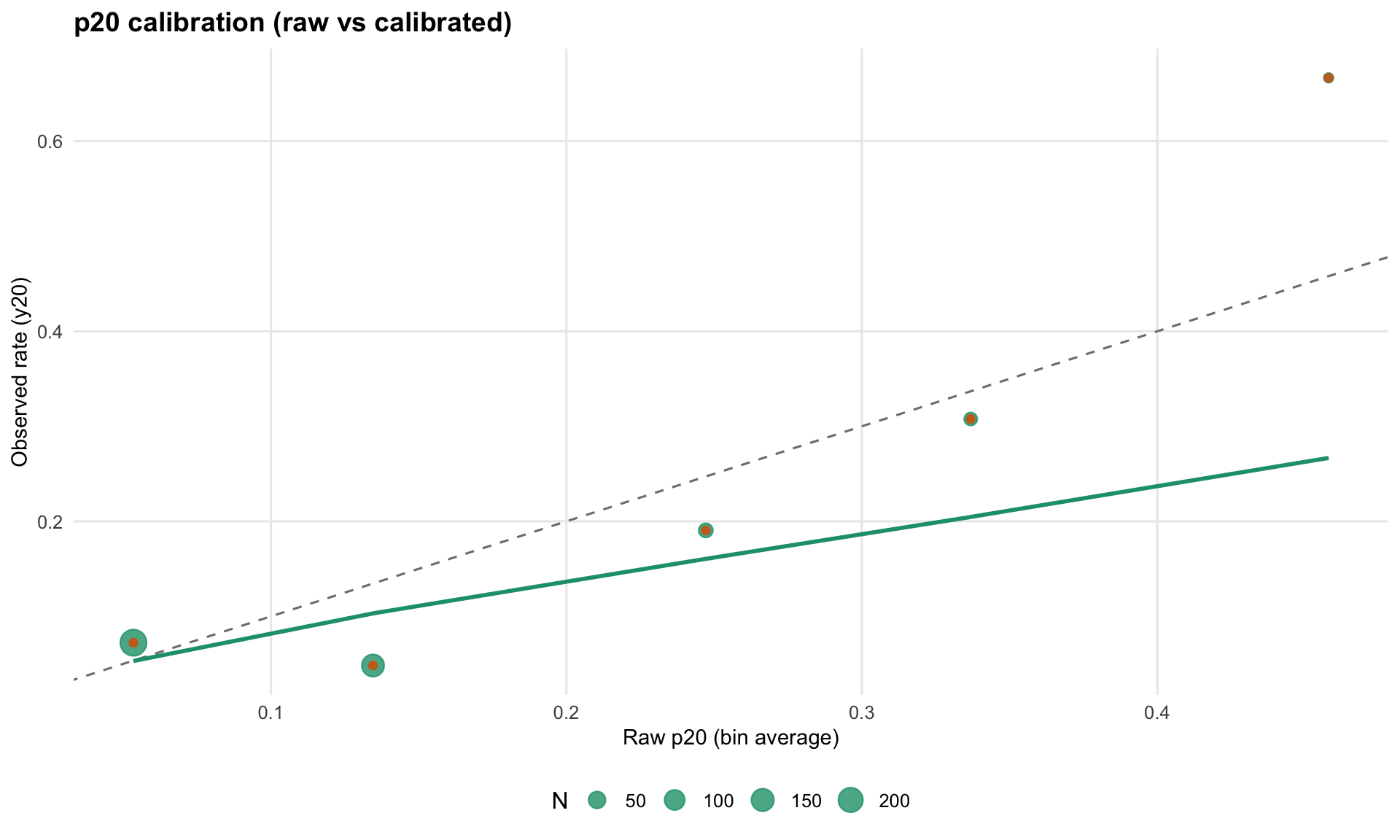
Calibration is applied to p20 only (probability of being below the 20th percentile cut). It does not change η or the rank ordering of students.
The frequentist approach treats PAT-based η as “truth” in Stage 2, ignoring Stage 1 uncertainty. This leads to underestimated standard errors for rating-only students, overconfident risk classifications (too narrow confidence intervals), and potential miscalibration (calibration slope ≠ 1.0).
Known Limitations
Ambiguous Date Format: Approximately 39% of PAT dates (332 of 849 non-empty dates) have ambiguous day/month values (both ≤12). The pipeline assumes d/m/Y (Australian standard) based on: Australian education context, 485 unambiguous dates validating d/m/Y, and EOY clustering patterns (94% Oct-Nov with d/m/Y vs 72% with m/d/Y). This cannot be validated without external verification.
Rating-Only Uncertainty (78% of Sample): Students with only teacher ratings have η estimated via soft probability labels derived from ordinal calibration. These estimates use frequentist approximation (normal distribution assumed), are influenced by rater severity bias (ICC_rater ≈ 24%), have higher standard errors than PAT-derived estimates, and may exhibit overconfidence (calibration slope ≠ 1.0).
Reference Group Caveats: PAT Maths 4th Edition (Year 1) uses 2022 Australian national norms (μ=99.5, σ=11.4). PAT Early Years (Foundation) uses ACER reference groups that are self-selecting and not nationally representative (per ACER documentation, June 2021). The interpretation of “10th percentile” differs between these populations.
PAT Timing Assumptions: η is defined as an end-of-year (EOY) attainment construct. Earlier PAT observations are less informative about EOY attainment. Time-decay variance increases with distance from reference date. Risk z-scores use NORM_FRAME_EOY (year-level specific).
Known Implementation Issues:
| Issue | Status | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Anchor selection | ⚠️ Uses latest-date logic | May not select record closest to EOY |
| Type gate validation | ⚠️ Tests product-standardised z | May not detect measurement differences |
| PAT Adaptive | ⚠️ Excluded | No ACER conversion tables available |
7 Discussion & Operational Roadmap
Design Choices
This run estimates η for 2410 students. The following design decisions are locked in:
- Construct: η targets end-of-year attainment (no growth projection; timing affects uncertainty only).
- Model: Hierarchical two-stage calibration with school-level random intercepts for rater severity.
- Rating-only prior: pat-empirical prior (estimated from PAT distribution in overlap calibration), not ACER. IPW disabled in mainline.
- Probabilities: p20 available as
p20_rawandp20_calibrated; not used to assign ACER risk bands.
These choices mostly affect rating-only students (the majority of the cohort). PAT-based students are much less sensitive.
Open Decisions
This report supports several downstream product decisions. These are not “statistical knobs”; they change how outputs should be communicated and used.
- Benchmark default: Should the primary view be ACER norms (
risk_band_acer) or cohort norms (risk_band_cohort)? - Teacher-facing outputs: Do we show a numeric η, only risk bands, or risk bands plus
p20_calibrated? - Operational criterion: Is “below 20th percentile” the right working definition of “behind expected”? (This is currently a placeholder pending external validation.)
- Borderline policy: How should Moderate be framed—middle severity (10th-20th) or “needs review” (uncertainty zone)?
- Governance for rating-only: Do we treat rating-only students as eligible for the same actions as PAT-confirmed students, or require follow-up assessment?
Validation Roadmap
Priority 1: External Criterion Validation
- Future outcomes: Collect Term 1 2026 PAT scores for longitudinal validation
- Growth trajectories: Analyse whether high-risk students show different growth patterns
- Teacher referral agreement: Compare risk classifications to independent teacher referrals
Priority 2: Calibration & Fairness
- Intervention response: Track which students benefit from intervention
- Demographic fairness: Check for systematic bias in risk classification by ATSI, LBOTE, SES
- Rater bias mitigation: Develop procedures to reduce school-level severity effects
Priority 3: Operational Refinement
- Borderline protocols: Establish clear procedures for students near cut-points
- Probability calibration: Validate p20 probabilities against actual outcomes
- Threshold adjustment: Recalibrate cuts based on external validation data
- Screening-outcome linkage: Analyse relationship between screening probe performance and outcome measures
- Growth analysis: Compare Occasion 1 vs Occasion 2 PAT trajectories by risk band
Lessons Learnt
Key methodological takeaways from the η estimation process:
- Sparse anchor data demands careful calibration: With only ~520 overlap students, the rating-to-PAT crosswalk is the critical bottleneck. Small changes to this sample (e.g., excluding a school) can shift risk prevalence materially.
- School-level effects are pervasive: School explains ~20% of rating variance and nearly 100% of PAT availability. Any model ignoring school structure will produce biased estimates.
- The Moderate band is inherently unstable: Bootstrap analysis shows 77.8% flip rate — this is a feature of having two close cut-points (10th and 20th percentile), not a model failure. Consider whether three bands are appropriate or whether a continuous probability (p20) better serves decision-making.
- Frequentist two-stage is pragmatic but imperfect: Treating Stage 1 η as known in Stage 2 underestimates uncertainty for rating-only students. A joint model would be theoretically superior but was computationally infeasible with current data sparsity.
- Date quality materially affects timing adjustments: The 39% ambiguous-date problem and wide administration windows mean σ_time estimates carry substantial uncertainty themselves.
8 Output Schema
Primary Output File
The primary output file student_eta_scored.parquet contains scale-score (η) and z-score (risk) representations:
Core fields (13 columns):
| Column | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
student_id |
chr | Student identifier |
year_level |
chr | Foundation or Year 1 |
school_id |
chr | School identifier |
eta_hat |
dbl | Point estimate of η (PAT scale-score units ~50-150) |
eta_se |
dbl | Standard error of η (scale-score units) |
eta_z |
dbl | Risk z-score: (η - μ_year) / σ_year using NORM_FRAME_EOY |
norm_mu |
dbl | Year-level norm mean (F: 92.4, Y1: 99.5) |
norm_sigma |
dbl | Year-level norm SD (F: 10.1, Y1: 11.4) |
risk_band |
fct | High / Moderate / Low |
is_borderline |
lgl | TRUE if near cut-point (±0.25 SD) |
source_flag |
chr | PAT_only / Rating_only / Both |
has_teacher_rating |
lgl | Has teacher rating available |
teacher_rating |
int | Teacher rating (1-5) |
Plausible values (10 columns): eta_pv_1 through eta_pv_10 — Independent draws from normal approximation for uncertainty propagation. Units: PAT scale-score (~50-150). Convert to z for risk: z_pv = (eta_pv - norm_mu) / norm_sigma.
Probability-First Output
The probability-first scheme produces student_scored_probability.parquet:
| Column | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
student_id |
chr | Student identifier |
eta_hat |
dbl | Point estimate of η |
eta_z |
dbl | Risk z-score |
p10 |
dbl | P(η < 10th percentile cut) |
p20 |
dbl | P(η < 20th percentile cut) |
action_tier |
fct | High / Review / Low (confidence) |
severity_level |
fct | Severe / Moderate / Mild/None |
probability_method |
chr | frequentist_approx |
9 Technical Appendix
Everything below is optional if you only need the operational story. It exists for auditability, reproducibility, and deeper investigation.
Appendix A: Technical Reference
A.1 Data Dictionaries
Raw Source: student_outcome.parquet
| Field | Data Type | Non-Missing | Missing % | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Identifier | character | 7,971 | 0.0 | Student GUID (unique identifier) |
| Standardised test result available | character | 1,387 | 82.6 | PAT form: PAT Early Years, PAT Maths Adaptive, PAT Maths (non-adaptive), or blank |
| Date of Testing | character | 692 | 91.3 | First PAT testing date (mixed formats) |
| Scaled Score | character | 632 | 92.1 | First PAT scaled score (as text) |
| Percentile Rank | character | 652 | 91.8 | First PAT percentile rank (as text) |
| EOY Standardised test result available | character | 475 | 94.0 | EOY PAT form (second administration) |
| EOY Date of Testing | character | 157 | 98.0 | EOY PAT testing date (mixed formats) |
| EOY Scaled Score | character | 238 | 97.0 | EOY PAT scaled score (as text) |
| EOY Percentile Rank | character | 180 | 97.7 | EOY PAT percentile rank (as text) |
| Achievement Scale | character | 2,358 | 70.4 | Teacher rating: 1 (well below) to 5 (well above expected achievement) |
Processed: student_outcome_pat.parquet
| Field | Data Type | Non-Missing | Missing % | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| student_id | character | 15,942 | 0.0 | Student GUID |
| year_level | character | 12,694 | 20.4 | Student year level: 'foundation' or 'year1' (standardised from grade field) |
| pat_occasion | integer | 15,942 | 0.0 | Testing occasion: 1 = chronologically first, 2 = chronologically second |
| pat_type | character | 951 | 94.0 | PAT form type (cleaned) |
| pat_date_raw | character | 849 | 94.7 | Original date string from source data |
| pat_date | Date | NA | NA | Parsed date (NA if suspect) |
| pat_scaled_score | numeric | 854 | 94.6 | Scaled score (numeric, placeholder 0/1 converted to NA) |
| pat_percentile | integer | 799 | 95.0 | Percentile rank (integer, suffix stripped) |
| pat_type_missing | logical | 15,942 | 0.0 | TRUE if valid score but PAT type was missing/wrong |
| pat_year_imputed | logical | 15,942 | 0.0 | TRUE if year was imputed for month-only date |
| pat_date_imputed | logical | 15,942 | 0.0 | TRUE if day was imputed for month-only date |
| pat_date_suspect | logical | 15,942 | 0.0 | TRUE if date flagged as suspect (1900, 2015, future, or >2 years old) |
| pat_score_percentile_mismatch | logical | 15,942 | 0.0 | TRUE if score exists without percentile or vice versa |
Processed: student_outcome_teacher.parquet
| Field | Data Type | Non-Missing | Missing % | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| student_id | character | 7,971 | 0.0 | Student GUID |
| year_level | character | 6,347 | 20.4 | Student year level: 'foundation' or 'year1' (standardised from grade field) |
| teacher_rating | integer | 2,358 | 70.4 | Teacher rating: 1-5 scale (integer) |
| teacher_rating_label | character | 2,358 | 70.4 | Full rating text (e.g., '3 - At expected achievement') |
| has_teacher_rating | logical | 7,971 | 0.0 | TRUE if student has a teacher rating |
A.2 Data Quality Gates
Gate 1a: Data Quality Audit
**Data Quality Checks:**
- PAT records: 15942
- Students with PAT: 781
- Students with teacher rating: 2358
- Overlap (both PAT and rating): 587
**PAT Type Summary:**
|pat_type | n_records| pct|
|:------------------------|---------:|----:|
|PAT Early Years | 510| 55.4|
|PAT Maths (non-adaptive) | 210| 22.8|
|PAT Maths Adaptive | 174| 18.9|
|PAT type missing | 26| 2.8|
|NA | 1| 0.1|
**Gate 1a Status:** PASSED Gate 1b: Indicator Coherence
Missingness Diagnostics
**Missingness Patterns:**Cluster Structure
**Cluster Inventory:**
- Total schools: 151
- Schools in overlap sample: A.3 Mathematical Model Specifications
Single-η Framework
η is ONE latent construct, measured in PAT scale-score units (~50-150). Different PAT products (Early Years, Maths, Adaptive) are different “thermometers” measuring the same underlying attainment. Risk z-scores are computed only at scoring time using NORM_FRAME_EOY.
Measurement Model
For students with PAT (scale-score outcome with time-decay uncertainty): \[\text{PAT}_{ij} \sim \text{Normal}(\eta_i + \delta_{\text{type}[j]}, \sqrt{\sigma^2_{\text{pat}} + \sigma^2_{\text{time}} \cdot \Delta t_{ij}^2 + \text{SE}^2_{\text{cond}[ij]}})\]
Where: - \(\eta_i\) is EOY attainment construct in PAT scale-score units - \(\delta_{\text{type}}\) captures systematic offsets between PAT products - \(\sigma^2_{\text{time}} \cdot \Delta t_{ij}^2\) is time-decay variance (uncertainty increases with distance from EOY) - \(\text{SE}_{\text{cond}}\) is the conditional standard error (known measurement error from ACER)
For students with teacher ratings: \[\text{Rating}_i \sim \text{OrderedLogistic}(\alpha + \lambda \eta_i + b_{\text{rater}[i]}, \tau)\]
Risk z-score Conversion (at scoring time only)
\[z_i = \frac{\eta_i - \mu_{\text{year}}}{\sigma_{\text{year}}}\]
Using NORM_FRAME_EOY: Foundation (μ=92.4, σ=10.1), Year 1 (μ=99.5, σ=11.4)
Hierarchical Structure
- \(\eta_i \sim \text{Normal}(\mu_{\text{yr}}, \sigma_\eta)\) — Student attainment (scale-score units)
- \(b_{\text{rater}} \sim \text{Normal}(0, \sigma_{\text{rater}})\) — Rater severity effects
Key Parameters
| Parameter | Description | Scale |
|---|---|---|
| η | Student latent attainment (EOY construct) | PAT scale-score units (~50-150) |
| μ_yr | Year-level population mean (F: ~92, Y1: ~100) | PAT scale-score units |
| σ_η | Between-student SD (~10-11 scale points) | Scale-score units |
| δ_type | PAT type offset (ref: Non-adaptive) | PAT scale-score units |
| σ_time | Time-decay uncertainty (scale points per year) | PAT scale-score units/year |
| λ | Rating discrimination slope | Probit units per scale-score |
| b_rater | Rater severity random effect | Probit units |
| σ_rater | Rater severity SD | Probit units |
Frequentist Implementation
Stage 1 (PAT model):
lmer(pat_scaled_score ~ year_level + pat_type + years_to_eoy + (1|school_id))Stage 2 (Rating calibration):
clmm(rating ~ 1 + eta_from_pat + (1|school_id))Stage 3 (Precision weighting): \[\hat{\eta}_{\text{combined}} = \frac{w_{\text{PAT}} \cdot \hat{\eta}_{\text{PAT}} + w_{\text{rating}} \cdot \hat{\eta}_{\text{rating}}}{w_{\text{PAT}} + w_{\text{rating}}}\]
Where \(w = 1 / \text{SE}^2\)
Appendix B: Diagnostic Detail
B.1 Bootstrap Reliability Analysis
Methodology
Bootstrap procedure (B=500 replicates):
- Cluster resampling: Sample schools with replacement, then all students within sampled schools
- Pipeline replay: Re-run frequentist estimation on each bootstrap sample
- Flip rate computation: For each student, calculate proportion of replicates with different risk band
Stability metrics:
- Flip rate: P(risk band changes across replicates)
- Stable students: Flip rate < 15% (target: 85% of sample)
- By distance to cut: Stratify by |z - cut_point|
Results Summary
**Overall Stability:**
- Mean flip rate: 0.039
- % stable (flip <15%): 96 %
**By Risk Class:**
Table: Flip rates by initial risk classification
|risk_band | n| flip_rate|
|:---------|----:|---------:|
|High | 10| 0.965|
|Low | 2308| 0.000|
|Moderate | 92| 0.902|
|NA | 5557| NaN|
**By Distance to Nearest Cut:**
Table: Flip rates by distance from decision boundary
**Transition Matrix:**
Table: Proportion of replicates in each risk bandInterpretation
High flip rate in Moderate band (77.8%) occurs because:
- Moderate students lie between two cuts (10th and 20th percentile)
- Measurement error can push estimates above or below either cut
- Bootstrap resampling amplifies uncertainty by varying the calibration sample
Recommendation: Treat Moderate risk as “borderline” requiring follow-up assessment, not a distinct stable category.
Session Information
R version 4.5.2 (2025-10-31)
Platform: aarch64-apple-darwin23.6.0
Running under: macOS Tahoe 26.2
Matrix products: default
BLAS: /opt/homebrew/Cellar/openblas/0.3.30/lib/libopenblasp-r0.3.30.dylib
LAPACK: /opt/homebrew/Cellar/r/4.5.2_1/lib/R/lib/libRlapack.dylib; LAPACK version 3.12.1
locale:
[1] en_AU.UTF-8/en_AU.UTF-8/en_AU.UTF-8/C/en_AU.UTF-8/en_AU.UTF-8
time zone: Australia/Sydney
tzcode source: internal
attached base packages:
[1] stats graphics grDevices utils datasets methods base
other attached packages:
[1] tibble_3.3.0 lme4_1.1-37 Matrix_1.7-3 patchwork_1.3.2
[5] lubridate_1.9.4 kableExtra_1.4.0 scales_1.4.0 ggplot2_4.0.0
[9] tidyr_1.3.1 dplyr_1.1.4 arrow_22.0.0 here_1.0.2
loaded via a namespace (and not attached):
[1] generics_0.1.4 xml2_1.4.0 lattice_0.22-6 stringi_1.8.7
[5] digest_0.6.37 magrittr_2.0.3 evaluate_1.0.5 grid_4.5.2
[9] timechange_0.3.0 RColorBrewer_1.1-3 fastmap_1.2.0 rprojroot_2.1.1
[13] jsonlite_2.0.0 purrr_1.1.0 viridisLite_0.4.2 codetools_0.2-20
[17] textshaping_1.0.3 Rdpack_2.6.4 reformulas_0.4.2 cli_3.6.5
[21] rlang_1.1.6 rbibutils_2.4 splines_4.5.2 bit64_4.6.0-1
[25] withr_3.0.2 yaml_2.3.10 tools_4.5.2 nloptr_2.2.1
[29] minqa_1.2.8 boot_1.3-31 assertthat_0.2.1 vctrs_0.6.5
[33] R6_2.6.1 lifecycle_1.0.4 stringr_1.5.2 htmlwidgets_1.6.4
[37] bit_4.6.0 MASS_7.3-65 pkgconfig_2.0.3 pillar_1.11.0
[41] gtable_0.3.6 Rcpp_1.1.0 glue_1.8.0 systemfonts_1.3.1
[45] xfun_0.53 tidyselect_1.2.1 rstudioapi_0.17.1 knitr_1.50
[49] farver_2.1.2 nlme_3.1-168 htmltools_0.5.8.1 labeling_0.4.3
[53] rmarkdown_2.29 svglite_2.2.2 compiler_4.5.2 S7_0.2.0 Model version: los_v1.0.0_20260121_seed20250116
Report generated: 2026-02-03 01:09:20 Report generated by the Latent Outcome Score pipeline. For questions, contact the ENSSA Analytics Team.